// ;earning purpose only everything that is been posted in the blog
This Tutorial shows you how to crack WPA securet networks
With the
popularity of wireless networks and mobile computing, an overall
understanding of common security issues has become not only relevant,
but very necessary for both home/SOHO users and IT professionals alike.
This article is aimed at illustrating current security flaws in
WEP/WPA/WPA2.
Successfully
cracking a wireless network assumes some basic familiarity with
networking principles and terminology, as well as working with
command-line tools. A basic familiarity with Linux can be helpful as
well.
Disclaimer: Attempting to access a network other than
your own, or one you have permission to use is illegal insome U.S.
jurisdictions. Speed Guide, Inc. are not to be held liable for any
damages resulting from the use or misuse of the information in this
article.
To successfully crack
WEP/WPA,
you first need to be able to set your wireless network card in
"monitor" mode to passively capture packets without being associated
with a network. This
NIC mode is driver-dependent, and only a relatively small number of network cards support this mode under Windows.
One of the best free utilities for monitoring wireless traffic and cracking WEP/WPA-PSK keys is the
aircrack-ng
suite, which we will use throughout this article. It has both Linux and
Windows versions (provided your network card is supported under
Windows). The aircrack-ng site has a comprehensive list of supported
network cards available here:
NIC chipset compatability list.
If your network card is not supported under Windows, one can use a free Linux Live CD to boot the
system.
BackTrack 3
is probably the most commonly used distribution, since it runs from a
Live CD, and has aircrack-ng and a number of related tools already
installed.
For this article, I am using aircrack-ng version
1.0 on a Linux partition (Fedora Core 10, 2.6 32-bit kernel) on my Sony
Vaio SZ-680 laptop, using the built-in Intel 4965agn network card. If
you're using the BackTrack 3 CD aircrack-ng is already installed, with
my version of linux it was as simple as finding it with:
yum search aircrack-ng
yum install aircrack-ng
The aircrack-ng suite is a collection of command-line programs aimed at
WEP and WPA-PSK key cracking. The ones we will be using are:
airmon-ng - script used for switching the wireless network card to monitor mode
airodump-ng - for WLAN monitoring and capturing network packets
aireplay-ng - used to generate additional traffic on the wireless network
aircrack-ng - used to recover the WEP key, or launch a dictionary attack on WPA-PSK using the captured data.
1. Setup (airmon-ng)
As
mentioned above, to capture network traffic wihtout being associated
with an access point, we need to set the wireless network card in
monitor mode. To do that under linux, in a terminal window (logged in as
root), type:
iwconfig (to find all wireless network interfaces and their status)
airmon-ng start wlan0 (to set in monitor mode, you may have to substitute wlan0 for your own interface name)
Note: You can use the su command to switch to a root account.
Other related Linux commands:
ifconfig (to list available network interfaces, my network card is listed as wlan0)
ifconfig wlan0 down (to stop the specified network card)
ifconfig wlan0 hw ether 00:11:22:33:44:55 (change the MAC address of a NIC - can even simulate the MAC of an associated client. NIC should be stopped before chaning MAC address)
iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor (to set the network card in monitor mode)
ifconfig wlan0 up (to start the network card)
iwconfig - similar to ifconfig, but dedicated to the wireless interfaces.
2. Recon Stage (airodump-ng)
This step assumes you've already set your wireless network interface in monitor mode. It can be checked by executing the
iwconfig command. Next step is finding available wireless networks, and choosing your target:
airodump-ng mon0
- monitors all channels, listing available access points and associated
clients within range. It is best to select a target network with strong
signal (PWR column), more traffic (Beacons/Data columns) and associated
clients (listed below all access points). Once you've selected a
target, note its Channel and BSSID (MAC address). Also note any STATION associated with the same BSSID (client MAC addresses).
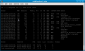 | 
running airodump-ng displays all wireless access points and associated clients in range, as well as MAC addresses, SSIDs, signal levels and other information about them. |
WEP
is much easier to crack than WPA-PSK, as it only requires data
capturing (between 20k and 40k packets), while WPA-PSK needs a
dictionary attack on a captured handshake between the access point and
an associated client which may or may not
work.
3. Capture Data (airodump-ng)
To
capture data into a file, we use the airodump-ng tool again, with some
additional switches to target a specific AP and channel. Most
importantly, you should restrict monitoring to a single channel to speed
up data collection, otherwise the wireless card has to alternate
between all channels. Assuming our wireless card is mon0, and we want to
capture packets on channel 6 into a text file called data:
airodump-ng -c 6 bssid 00:0F:CC:7D:5A:74 -w data mon0 (-c6 switch would capture data on channel 6, bssid 00:0F:CC:7D:5A:74 is the MAC
address of our target access point, -w data specifies that we want to
save captured packets into a file called "data" in the current
directory, mon0 is our wireless network adapter)
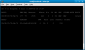 | 
Running airodump-ng on a single channel targeting a specific access point |
Notes:
You typically need between 20,000 and 40,000 data packets to successfully recover a
WEP key.
One
can also use the "--ivs" switch with the airodump-ng command to capture
only IVs, instead of whole packets, reducing the required disk space.
However, this switch can only be used if targeting a
WEP network, and renders some types of attacks useless.
4. Increase Traffic (aireplay-ng) - optional step for WEP cracking
An
active network can usually be penetrated within a few minutes. However,
slow networks can take hours, even days to collect enough data for
recovering the
WEP key.
This
optional step allows a compatible network interface to inject/generate
packets to increase traffic on the wireless network, therefore greatly
reducing the time required for capturing data. The aireplay-ng
command should be executed in a separate terminal window, concurrent to
airodump-ng. It requires a compatible network card and driver that
allows for injection mode.
Assuming your network card is capable of injecting packets, in a separate terminal window try:
aireplay-ng -3 -b 00:0F:CC:7D:5A:74 -h 00:14:A5:2F:A7:DE -x 50 wlan0
-3 --> this specifies the type of attack, in our case ARP-request replay
-b ..... --> MAC address of access point
-h ..... --> MAC address of associated client from airodump
-x 50 --> limit to sending 50 packets per second
wlan0 --> our wireless network interface
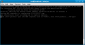 | 
aireplay-ng allows for injecting packets to greatly reduce the time required to recover a WEP key |
Notes:
To test whether your
nic is able to inject packets, you may want to try: aireplay-ng -9 wlan0. You may also want to read the information available
-here-.
To see all available replay attacks, type just: aireplay-ng
5. Crack WEP (aircrack-ng)
WEP
cracking is a simple process, only requiring collection of enough data
to then extract the key and connect to the network. You can crack the
WEP key while capturing data. In fact, aircrack-ng will re-attempt cracking the key after every 5000 packets.
To attempt recovering the
WEP key, in a new terminal window, type:
aircrack-ng data*.cap (assuming your capture file is called data...cap, and is located in the same directory)
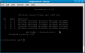 | 
aircrack-ng can successfully recover a WEP key with 10-40k captured packets. The retreived key is in hexadecimal, and can be entered directly into a wireless client omitting the ":" separators |
Notes:
If
your data file contains ivs/packets from different access points, you
may be presented with a list to choose which one to recover.
Usually, between 20k and 40k packets are needed to successfully crack a
WEP key. It may sometimes work with as few as 10,000 packets with short keys.
6. Crack WPA or WPA2 PSK (aircrack-ng)
WPA, unlike
WEP rotates the network key on a per-
packet basis, rendering the
WEP
method of penetration useless. Cracking a WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK key requires
a dictionary attack on a handshake between an access point and a
client. What this means is, you need to wait until a wireless client
associates with the network (or deassociate an already connected client
so they automatically reconnect). All that needs to be captured is the
initial "four-way-handshake" association between the access point and a
client. Essentially, the weakness of WPA-PSK comes down to the
passphrase. A short/weak passphrase makes it vulnerable to dictionary
attacks.
To successfully crack a WPA-PSK network, you first need a
capture file containing handshake data. This can be obtained using the
same technique as with
WEP in step 3 above, using airodump-ng.
You may also try to deauthenticate an associated client to speed up this process of capturing a handshake, using:
aireplay-ng --deauth 3 -a MAC_AP -c MAC_Client mon0 (where MAC_IP is the MAC address of the access point, MAC_Client is the MAC address of an associated client, mon0 is your wireless NIC).
The command output looks something like:
12:34:56 Waiting for beakon frame (BSSID: 00:11:22:33:44:55:66) on channel 6
12:34:56 Sending 64 directed DeAuth. STMAC: [00:11:22:33:44:55:66] [ 5:62 ACKs]
Note the last two numbers in brackets [ 5:62 ACKs] show the number of acknowledgements received from the client
NIC
(first number) and the AP (second number). It is important to have some
number greater than zero in both. If the first number is zero, that
indicates that you're too far from the associated client to be able to
send deauth packets to it, you may want to try adding a reflector to
your antenna (even a simple manilla folder with aluminum foil stapled to
it works as a reflector to increase range and concentrate the signal
significantly), or use a larger antenna.
 | 
Simple
antenna reflector using aluminum foil stapled to a manilla folder can
concentrate the signal and increase range significantly. For best
results, you'll have to place the antenna exactly in the middle and
change direction as necessary. Of course there are better reflectors out there, a parabolic reflector would offer even higher gain, for example. |
Once
you have captured a four-way handshake, you also need a large/relevant
dictinary file (commonly known as wordlists) with common passphrases.
See related links below for some wordlist links.
You can, then
execute the following command in a linux terminal window (assuming both
the dictionary file and captured data file are in the same directory):
aircrack-ng -w wordlist capture_file (where wordlist is your dictionary file, and capture_file is a .cap file with a valid WPA handshake)
Additional Notes:
Cracking
WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK only needs 4 packets of data from the network (a
handshake). After that, an offline dictionary attack on that handshake
takes much longer, and will only succeed with weak passphrases and good
dictionary files. A good size wordlist should be 20+ Megabytes in
size, cracking a strong passphrase will take hours and is CPU intensive.
Cracking
WPA/WPA2
usually takes many hours, testing tens of millions of possible keys for
the chance to stumble on a combination of common numerals or dictionary
words. Still, a weak/short/common/human-readable passphrase can be
broken within a few minutes using an offline dictionary attack. My
record time was less than a minute on an all-caps 10-character
passphrase using common words with less than 11,000 tested keys! A
modern laptop can process over 10 Million possible keys in less than 3
hours.
WPA hashes the network key using the wireless access point's
SSID as salt. This prevents the statistical key-grabbing techniques that broke
WEP, and makes hash precomputation more dificult because the specific
SSID
needs to be added as salt for the hash. There are some tools like
coWPAtty that can use precomputed hash files to speed up dictionary
attacks. Those hash files can be very effective (sicne they're much less
CPU intensive and therefore faster), but quite big in size. The
Church of WiFi has computed hash tables for the 1000 most common SSIDs against a million common passphrases that are 7Gb and 33Gb in size...
Conclusion
As demonstrated above,
WEP cracking
has become increasingly easier over the years, and what used to take
hundreds of thousands packets and days of capturing data can be
accomplished today within 15 minutes with a mere 20k data frames.
WPA/WPA2-PSK
encryption is holding its ground if using a strong, long key. However, weak passphrases are vulnerable to dictionary attacks.
WPA/WPA2 may be on borrowed time as well, according to some
recent news.




